Cloud security strategy

Cloud computing presents unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, rendering it a smart option for organizations aiming to optimize their IT infrastructure. Nevertheless, as cloud technology proliferates, it ushers in a parallel escalation in potential security susceptibilities. Read on to explore the significance of cloud security and the key components of a proficient cloud security strategy. We’ll also dive into various solutions and lay out the best practices associated with cloud security.

Definition of cloud security
Cloud security pertains to the comprehensive framework of policies, technologies, and practices organizations employ to safeguard their data, applications, and infrastructure hosted within cloud environments. It encompasses a wide array of measures that are designed to shield against potential threats, including data breaches, unauthorized access, service interruptions, and other hazards that can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of cloud-based resources.
Why is cloud security important?
Ensuring robust cloud security is vital for several reasons:
- Data protection: One of the most critical aspects of cloud security is safeguarding sensitive data. Cloud storage often contains valuable business and customer information, including financial records, intellectual property, personal identifiable information (PII), and more. Failing to secure this data can lead to data breaches, which can have severe legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
- Business continuity: Many organizations rely heavily on cloud services for their day-to-day operations. Ensuring the availability and resilience of these services is essential to prevent downtime, which can result in significant financial losses. Effective cloud security measures help mitigate the risk of service interruptions due to cyberattacks, technical failures, or natural disasters.
- Compliance requirements: Various industries have strict regulatory requirements regarding data protection and privacy. For instance, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the healthcare sector have stringent data security provisions. Proper cloud security measures help organizations meet these compliance standards, reducing the risk of fines, legal action, and damage to their reputation.

- Reputation management: A security breach can tarnish an organization's reputation and erode trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders. News of a data breach can spread quickly, leading to negative publicity and a loss of credibility. A strong commitment to cloud security demonstrates an organization's dedication to protecting sensitive information and can help maintain trust in the brand.
- Cost control: Effective cloud security can help prevent unexpected expenses associated with security incidents and data loss. The financial impact of a security breach can be significant, including costs related to incident response, regulatory fines, legal fees, and compensation to affected parties. Investing in proactive security measures is often more cost-effective than dealing with the aftermath of a breach.
- Intellectual property protection: Many businesses rely on cloud infrastructure for the storage and processing of intellectual property, proprietary algorithms, and trade secrets. Ensuring the security of these assets is essential to maintain a competitive edge and prevent unauthorized access or theft.
- Supply chain security: In today's interconnected business landscape, many organizations rely on cloud-based services from various vendors. Ensuring the security of these services and assessing the security posture of third-party providers is crucial to prevent security gaps in the supply chain.
- Data sovereignty: Organizations may be subject to legal requirements that dictate where their data can be stored and processed. Cloud security measures, including encryption and access controls, help organizations maintain compliance with data sovereignty regulations.
- Scalability and elasticity: As organizations scale their cloud infrastructure, ensuring security scales proportionally is essential. Cloud security solutions need to adapt to changing requirements and handle increased workloads without compromising protection.
- Continuous monitoring and threat detection: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, making continuous monitoring and threat detection crucial. Cloud security solutions provide real-time insights into potential security threats, allowing organizations to respond quickly and effectively.

10 elements of an effective cloud security strategy
A comprehensive cloud security strategy should encompass various elements to address different security aspects. Here are ten key components to consider:
1. Shared responsibility
- Understanding the model: Familiarize yourself with the specific security measures your cloud provider offers by default, and what additional measures you need to put in place.
- Documentation: Clearly document and regularly update roles and responsibilities to ensure all team members are aligned.
2. Visibility
- Centralized dashboard: Use a unified dashboard that offers a comprehensive view of all cloud resources, configurations, and activity logs.
- Access control: Ensure that only authorized personnel can view and manage sensitive data.
3. Monitoring
- Continuous monitoring: Ensure that monitoring tools are always up to date and are examining all relevant metrics and logs.
- Integration with SIEM: Integrate cloud logs with a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system for centralized security intelligence.
4. Managing Vulnerabilities
- Scheduled scans: Establish a regular cadence for vulnerability scans and updates.
- Third-party software: Regularly assess third-party software or services integrated with your cloud resources.
5. Response
- Simulation: Regularly conduct drills or simulated incidents to test and refine the incident response strategy.
- Communication: Have a clear communication plan, both internally and with external stakeholders, for when incidents occur.
6. Detection
- Machine learning and AI: Employ ML-based anomaly detection to identify new and emerging threats.
- Regular review: Periodically review and refine the parameters and thresholds set for alerts.
7. Resilience
- Geographic diversity: Distribute backups across various geographical locations to mitigate the risk from regional outages.
- Testing: Regularly test failover and backup mechanisms to ensure they work as expected.
8. Data encryption
- Key rotation: Regularly change encryption keys and follow best practices for key management.
- Use updated protocols: Always use updated and secure encryption protocols.
9. Endpoint protection
- Device management: Employ a mobile device management (MDM) or endpoint management solution to have control over the devices accessing cloud resources.
- Regular updates: Ensure all endpoints have the latest security patches and updates.
10. DevSecOps
- Security training: Provide regular training for developers on secure coding practices.
- Automated security testing: Integrate automated security tests into the CI/CD pipeline to catch potential vulnerabilities early.
Types of cloud security solutions
The diverse realm of cloud security solutions encompasses a wide array of options, each serving a unique purpose:

| Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP) | CWPPs offer comprehensive security by continuously monitoring and detecting threats across diverse cloud environments, ensuring protection in both online and physical locations. |
| Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) | CNAPPs streamline complexity by integrating multiple tools into a single software package.
They provide end-to-end security for cloud applications throughout the entire development-to-production lifecycle, ensuring robust protection. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | SIEM solutions enhance visibility by aggregating data from various sources within an environment.
They serve as a foundation for identifying malicious activities, generating reports, and supporting efficient incident response. |
| Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) | CIEM solutions are invaluable for managing entitlements across an organization's entire spectrum of cloud infrastructure resources.
Their primary goal is to mitigate the risks associated with unintentional and unchecked permissions granted to cloud resources. |
| Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) | CSPM leverages automation to identify and remediate risks across cloud infrastructures.
It excels in risk visualization, assessment, incident response, compliance monitoring, and seamless integration with DevOps processes. |
| Container security | Container security solutions are tailored to safeguard containers from cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
They extend protection across the entire CI/CD pipeline, deployment infrastructure, and supply chain. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | DLP solutions play a crucial role in preventing data loss, leakage, or misuse through various means such as breaches, unauthorized transmissions, and improper utilization. |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | IAM represents a framework that enables precise control over access to systems, networks, and assets based on each user's unique identity, enhancing security and access management. |
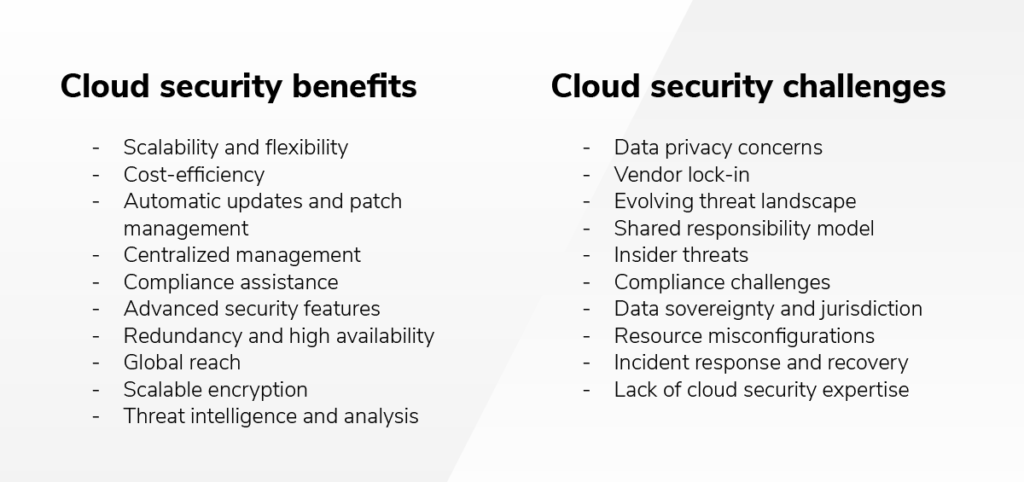
Cloud security benefits and challenges
The transition of IT infrastructure and services to cloud-based platforms has become commonplace for organizations globally. Although the cloud offers many advantages, it concurrently introduces a distinct array of security considerations. Let’s delve into the merits and complexities of cloud security, providing insights into the ever-evolving terrain of protecting digital assets within cloud environments.
Cloud security benefits
Scalability and flexibility:
- Cloud security solutions can scale up or down to meet the changing needs of an organization.
- Resources can be allocated dynamically to address emerging security threats effectively.
- Organizations can adapt security measures to accommodate fluctuations in workloads and demand, ensuring that security remains robust even during peak usage periods.
Cost-efficiency:
- Cloud security can be cost-effective compared to maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models eliminate the need for substantial upfront capital expenditures.
- Cloud security services often bundle multiple security solutions, reducing costs and simplifying the implementation of various security measures.
Automatic updates and patch management:
- Cloud providers take on the responsibility of maintaining and updating their infrastructure, including security patches and updates.
- This proactive approach to security ensures that organizations benefit from the latest defenses against evolving threats without the need for extensive manual intervention.
- Automatic updates help reduce the risk of vulnerabilities due to outdated software.
Centralized management:
- Cloud security solutions typically provide centralized management interfaces.
- Organizations can monitor and manage their security measures from a single dashboard, improving operational efficiency.
- Centralized management enhances visibility into security events and simplifies the enforcement of security policies across the entire cloud environment.
Compliance assistance:
- Many cloud providers offer compliance certifications and tools to help organizations meet regulatory requirements.
- Certifications such as SOC 2, HIPAA, and PCI DSS demonstrate a commitment to security and data protection.
- Compliance assistance features provided by cloud services can simplify the process of adhering to industry-specific and regional regulations, saving organizations time and effort.
Advanced security features:
- Cloud security solutions often come with advanced security features, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and threat intelligence.
- These features provide proactive threat detection and prevention capabilities, reducing the likelihood of security incidents.
Redundancy and high availability:
- Cloud providers typically offer redundancy and high availability features.
- Data and applications are often replicated across multiple data centers or regions, reducing the risk of downtime due to hardware failures or disasters.
Global reach:
- Cloud security services are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making them suitable for organizations with a global presence.
- Employees can securely access resources and applications from remote locations, promoting flexibility and productivity.
Scalable encryption:
- Cloud providers offer robust encryption capabilities to protect data both at rest and in transit.
- Encryption can be easily scaled to meet the specific security requirements of different workloads and data types.
Threat intelligence and analysis:
- Cloud security platforms often incorporate threat intelligence feeds and analysis tools.
- These tools provide organizations with insights into emerging threats and trends, allowing for proactive threat mitigation.
Cloud security challenges
Data privacy concerns:
- The storage of sensitive data in the cloud raises concerns about data privacy and control.
- Organizations must ensure that their cloud provider has robust data encryption mechanisms to protect data both at rest and in transit.
- Effective access control mechanisms are crucial to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Vendor lock-in:
- Relying heavily on a specific cloud provider's services can lead to vendor lock-in.
- Migrating to another cloud provider or reverting to on-premises infrastructure can be challenging and costly.
- To mitigate this risk, organizations should design their cloud architecture with portability in mind, adopting standards and best practices that promote flexibility.
Evolving threat landscape:
- The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated and frequent.
- Organizations must stay vigilant and adapt their security measures accordingly.
- Continuous monitoring, threat intelligence, and a proactive security posture are essential to keep pace with emerging threats.
Shared responsibility model:
- Understanding and managing the shared responsibility model can be complex.
- Cloud providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and configurations.
- Defining and managing the division of responsibilities effectively is crucial to prevent security gaps.
Insider threats:
- Insider threats, whether stemming from malicious intent or unintentional actions, represent a significant risk to cloud security.
- Organizations must establish strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) protocols to control access to cloud resources.
- Implementing effective Data Loss Prevention (DLP) strategies is vital to detect and mitigate potential threats from within the organization.
Compliance challenges:
- Meeting regulatory and compliance requirements can be challenging in the cloud, especially for organizations in heavily regulated industries.
- Cloud providers may offer compliance certifications, but customers are still responsible for configuring their environments to meet specific compliance standards.
- Compliance in the cloud requires a deep understanding of both the organization's obligations and the capabilities and limitations of the cloud provider's services.
Data sovereignty and jurisdiction:
- The location of data stored in the cloud may have legal implications, especially regarding data sovereignty and jurisdiction.
- Organizations must navigate complex legal and regulatory landscapes to ensure they comply with laws governing data storage and processing in various regions.
Resource misconfigurations:
- Misconfigurations of cloud resources, such as storage buckets or firewall rules, can expose sensitive data and services to potential threats.
- Organizations need robust security practices, including automated scanning and auditing of cloud configurations, to detect and remediate misconfigurations promptly.
Incident response and recovery:
- Developing and implementing an effective incident response and recovery plan specific to the cloud environment is crucial.
- Organizations must be prepared to quickly identify and respond to security incidents, minimize damage, and recover their systems and data.
Lack of cloud security expertise:
- A shortage of skilled cloud security professionals can be a challenge for organizations.
- Ensuring that staff have the necessary knowledge and skills to manage and secure cloud environments is essential.
- SADA provides comprehensive services aimed at addressing the shortage of skilled professionals in cloud security. SADA security experts offer strategic guidance and implementation support, helping organizations fortify their security posture by deploying the latest tools, practices, and frameworks. By partnering with SADA, organizations can bridge the gap in cloud security talent, enhancing their resilience against evolving cyber threats while maximizing the potential of their cloud infrastructure. Contact us for a Cloud Security Confidence Assessment and we’ll evaluate your current security posture and give you actionable recommendations to reduce risks and prepare for threats.
How to properly secure the cloud
To ensure proper cloud security, organizations should follow best practices, including:
- Conducting regular security assessments.
- Training staff on security awareness.
- Enforcing strong authentication and access controls.
- Implementing encryption and data classification.
- Developing and testing incident response plans.


Standards-based cloud security guidance
Several industry standards and frameworks, such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO/IEC 27001, guide cloud security. These standards can help organizations establish a strong foundation for their cloud security strategy.
FAQ
The five essential components of a strong security strategy are:
- Data encryption and privacy: By implementing robust encryption methods, you’ll be able to safeguard sensitive data both in transit and at rest within your cloud environment.
- Identity and access management (IAM): Control access to your cloud resources by implementing measures like multi-factor authentication (MFA), least privilege access, and centralized identity management.
- Comprehensive security controls: By employing a range of security controls and tools like firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, anti-malware solutions, and continuous monitoring solutions, you’ll be well equipped to combat emerging threats.
- Regular security audits and compliance: You can evaluate the effectiveness of your security measures, identify weaknesses, and ensure compliance by conducting frequent security audits and assessments.
- Incident response and disaster recovery: By developing a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines procedures to detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents or data breaches, you’ll be able to ensure business continuity in case of unexpected disruptions or cyber attacks.
LET'S TALK
Our expert teams of consultants, architects, and solutions engineers are ready to help with your bold ambitions, provide you with more information on our services, and answer your technical questions. Contact us today to get started.

