Table of contents
- Google Bard vs ChatGPT
- Google Bard
- ChatGPT
- Bard vs ChatGPT: a comparison
- An argument for Bard’s user experience
- Bard is built for research, while ChatGPT is often the better writer
- Bard vs ChatGPT: how to decide between the two
- Considerations and caveats when using AI chatbots
- Should your organization use Google Bard or ChatGPT?
The stunning breakthroughs we’ve seen with the rise of generative AI rest upon the foundation of Large Language Models, or LLMs, which are designed to detect and predict patterns in written human communication. Google Bard (recently renamed Gemini) and Open AI’s ChatGPT represent two of the most widely used LLMs. While they operate according to shared principles, there are differences between the two. In this post, we’ll explore their capabilities, applications, ethical implications, and their potential impact on the AI landscape.
Google Bard vs ChatGPT
| Aspect | Google Bard | ChatGPT |
| Chatbot | Developed by Google, Bard AI is Google’s venture into advanced conversational AI. | Developed by OpenAI, in partnership with Microsoft, ChatGPT is celebrated for its natural language generation abilities. |
| Company | OpenAI, supported by Microsoft | |
| Sources of data | Bard’s training data, sourced from Infiniset, includes Common Crawl, Wikipedia, and web-based documents. Its standout feature is real-time web searches for the most current answers and research. | ChatGPT was trained on a wide range of text sources, including Common Crawl, Wikipedia, books, articles, and more. Its dataset ends in 2021. |
| Language model | Powered by the PaLM 2 language model, Bard AI boasts advanced conversational abilities and a robust grasp of context. | ChatGPT is based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, with the option of ChatGPT Plus subscription offering access to the even more advanced GPT-4 model. |
| Price | Presently, Google Bard offers its services for free to all users. | ChatGPT is available for free, with the ChatGPT Plus subscription plan priced at $20 per month, granting access to additional features. |
| Launch date | March 2023 | November 2022 |
| Subscription plans | None currently | ChatGPT Plus for enhanced features |
| Sign-in requirements | A Google account is necessary for sign-up and joining the waitlist for Google Bard. | ChatGPT does not require a specific email address, and there is currently no waitlist. |
| Language support | Offers support for more than 40 languages, including English, Spanish, Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Japanese, Turkish, Portuguese, Hindi, Bengali, German, Indonesian, Marathi, Vietnamese, and many others. | Boasts support for over 95 languages, including English, Spanish, Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Japanese, Turkish, Portuguese, Hindi, Bengali, German, Indonesian, Marathi, Vietnamese, and more. |
Google Bard
Introduced by Alphabet Inc. in March 2023, Bard stands as Google’s response to ChatGPT. Bard represents an advanced conversational AI solution, benefiting from Google’s expertise in machine learning, natural language processing, and state-of-the-art AI technologies. Capitalizing on decades of research, Google developed Bard to enhance the user experience for both individual users and businesses. Bard is currently available for free, without a premium subscription program like ChatGPT Plus. Google’s commitment to ongoing improvements ensures that this groundbreaking chatbot will continue to evolve, becoming more robust and efficient over time.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is the brainchild of OpenAI, a pioneering research organization dedicated to advancing artificial intelligence. This AI chatbot stands out for its ability to generate responses that closely mimic human language. Its versatility extends to various applications, such as content creation, programming assistance, and general-purpose chat support.
Since its inception, OpenAI has remained committed to refining and enhancing its chatbot. In March 2023, the company introduced GPT-4, a significant upgrade. GPT-4 excels in producing more nuanced text responses and exhibits a substantially improved ability to grasp contextual nuances compared to GPT-3.5. ChatGPT offers a free version powered by GPT-3.5, whereas GPT-4 is presently accessible exclusively through the ChatGPT Plus subscription plan. There are aspirations to eventually make GPT-4 available as a free tool.
Now, let’s delve into the technologies underpinning these formidable chatbots.

Bard vs ChatGPT: a comparison
Anyone who is interested in establishing a generative AI practice at the organizational level has a set of choices to make between two compelling LLMs that are rapidly evolving before our eyes.
Before you make your decision, it’s wise to take stock of what it is you wish to achieve with generative AI. Are you looking for assistance with producing marketing materials? Do you want to provide backup for your IT department, with a generative AI solution that assists with code?
When you add generative AI to your tech stack, you’re integrating a solution that will continue to grow and develop new capabilities, which means you’re opening your organization up to quickly evolve, as well. Crucially, your role is to define the direction of that evolution in alignment with your business goals. Starting from that vision, you’re in a better position to weigh the pros and cons of Google Bard and ChatGPT.
Sources of data
Bard leverages the Infiniset dataset, a comprehensive resource comprising Common Crawl, Wikipedia, various publicly available documents, and web-based conversations. Bard’s real-time web search capability sets it apart, as it ensures access to the most current information and research findings.
ChatGPT’s training corpus is diverse, drawing from sources including Common Crawl, Wikipedia, books, articles, documents, and publicly available Internet content. It’s crucial to note, however, that the data it was trained on only extends up to 2021, potentially limiting its knowledge of the latest world events and research.
Language model
Google Bard: Powered by the PaLM 2 language model, Bard AI boasts advanced conversational abilities and a robust grasp of context.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT is based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, with the option of ChatGPT Plus subscription offering access to the even more advanced GPT-4 model.
Pricing
Google Bard: Presently, Google Bard offers its services for free, making it accessible to all users.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT is available for free, with the ChatGPT Plus subscription plan priced at $20 per month, granting access to additional features.
Launch dates
Google Bard: Google Bard made its debut in March 2023, showcasing Google’s latest advancements in conversational AI.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT was introduced in November 2022 and has since undergone continuous refinement.
Subscription plans
Google Bard: As of now, Google Bard does not provide a subscription plan, ensuring free access to its capabilities.
ChatGPT: OpenAI offers the ChatGPT Plus subscription plan for users seeking enhanced features and capabilities.
Sign-in requirements
Google Bard: A Google account is necessary for sign-up and joining a waitlist to use Bard.
ChatGPT: ChatGPT does not require a specific email address, and there is currently no waitlist, making it easily accessible.
Language support
Google Bard: Offers support for more than 40 languages, encompassing English, Spanish, Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Japanese, Turkish, Portuguese, Hindi, Bengali, German, Indonesian, Marathi, Vietnamese, and many others.
ChatGPT: Boasts support for over 95 languages, including English, Spanish, Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Japanese, Turkish, Portuguese, Hindi, Bengali, German, Indonesian, Marathi, Vietnamese, and more.
An argument for Bard’s user experience
We’ve been impressed by Bard’s user experience. Its user-friendly interface not only boasts a visually appealing design but also presents text in a highly digestible format, in contrast to ChatGPT’s chunkier text presentation. Bard goes beyond just aesthetics; it allows you to edit your questions post-submission and offers multiple response options for your convenience.
For those who prefer auditory interaction, Bard offers a unique feature: a sound icon in the top-right corner, enabling you to listen to Bard read its responses aloud.
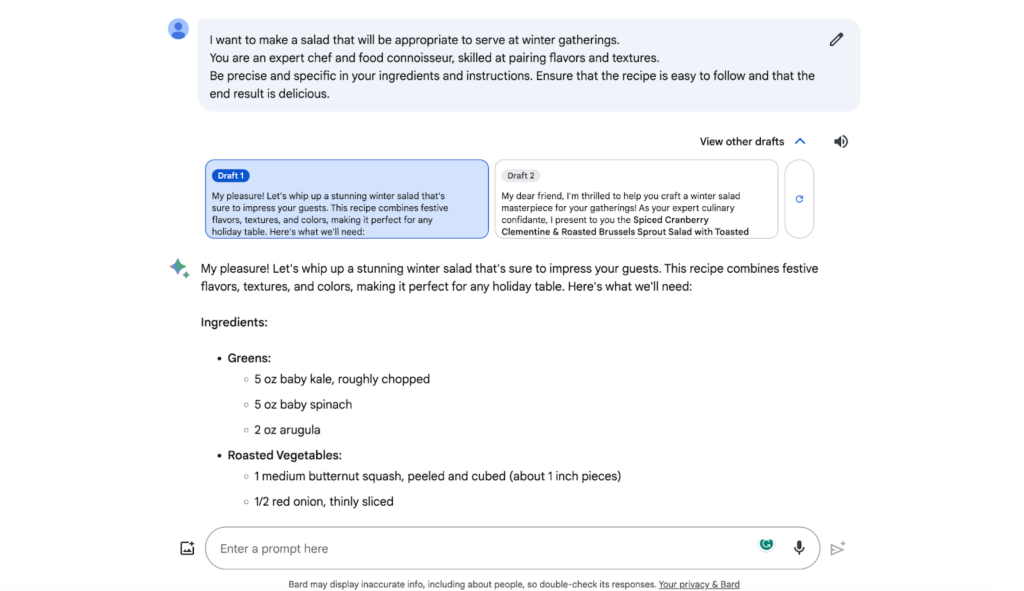
By clicking the sound icon, users can listen to Bard read its responses out loud
One of Bard’s standout features is its incorporation of a “Google it” call-to-action (CTA) with every response, facilitating easy source verification. Its seamless integration with Google Workspace simplifies the process of transferring Bard’s responses to your Gmail or Google Docs.
Both Bard and ChatGPT provide access to your entire conversation history via a side panel, allowing you to easily share conversations with friends and colleagues. Bard distinguishes itself by allowing you to modify each response without the need for creating an entirely new prompt. A click on the Modify icon lets you adjust elements like response length or tone, instantly generating a revised answer that aligns with your preferences.
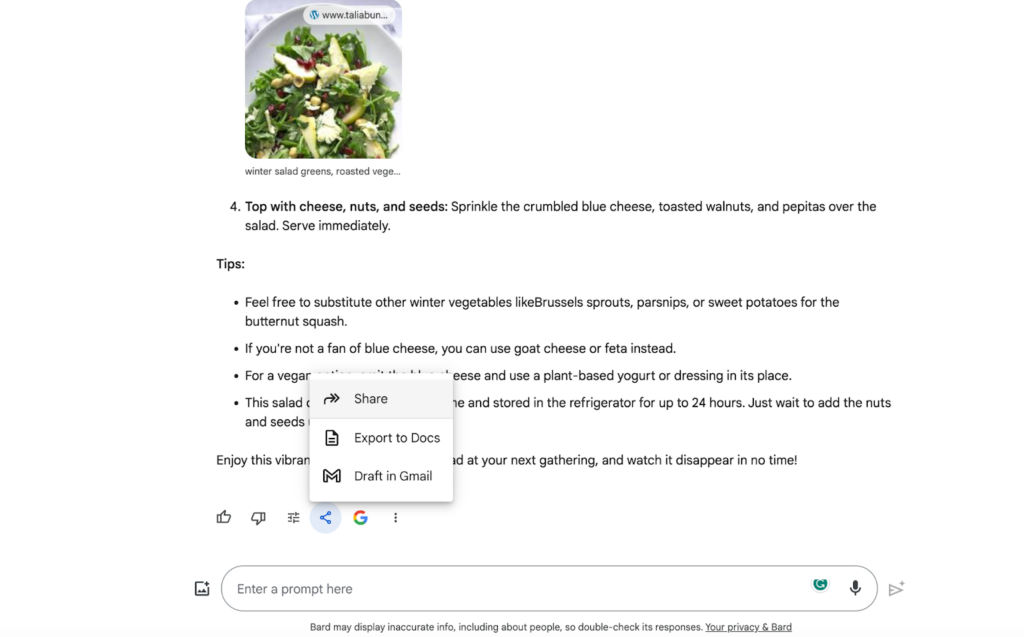
Easily share Google Bard conversations with friends and colleagues
ChatGPT offers a solution to streamline your interactions by allowing you to include custom instructions. This way, ChatGPT automatically considers specific preferences, such as a casual or professional tone, without the need to specify them in every prompt. While Bard sets the benchmark for user-friendliness, ChatGPT offers flexibility with customization options.
Bard is built for research, while ChatGPT is often the better writer
Let’s start with an acknowledgement that both Bard and ChatGPT sometimes encounter logic issues. That said, they’re continuing to improve, even demonstrating improvements in the time between when we first started writing this blog post and when we got closer to the final draft.
We asked Bard and ChatGPT the same simple question and compared the results. Take a look for yourself.
Bard:
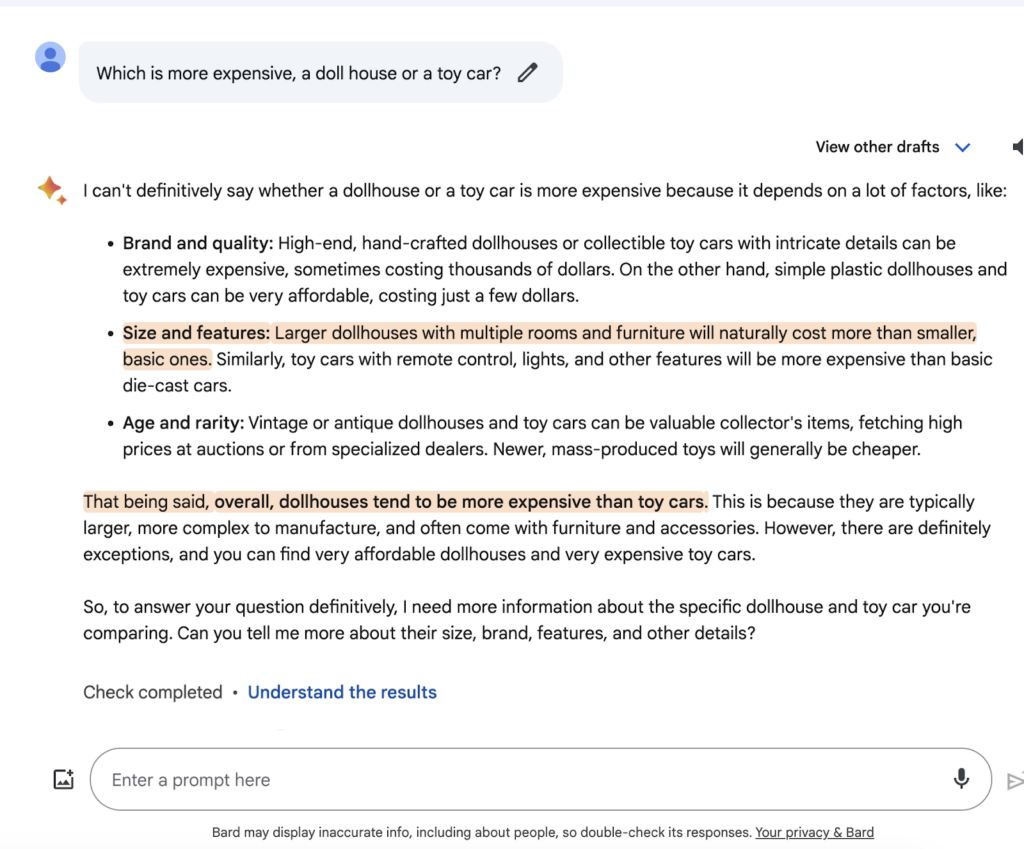
Here’s how ChatGPT responded to the same question.

You’ll notice that Bard offered some text highlighted in orange. By clicking this text, you can cross-reference the output using Google search, a feature we like a lot. Bard looks like a great contender for research-heavy writing, with tools integrated into the output that allow you to tap into search functionality.
ChatGPT, on the other hand, may be better for certain tasks that involve a higher degree of wordsmithing. It really just depends on your area of focus. GPT enjoys a reputation as the industry standard for natural language tasks and is the driving force behind various AI tools such as Jasper, Copy.ai, and Bing’s AI tools. Its expertise lies in generating text based on statistical patterns, and as part of ChatGPT, it serves as a chatbot while also excelling in roles such as summarization and translation on a more text-centric level.
It’s worth your time to play around with both ChatGPT and Bard to see which serves you better as a writing tool. We asked each chatbot to compose a tweet. GPT-4 adhered closely to the conventions of tweet writing, including character count limitations, emojis, and hashtags. Although not perfect, it delivered a working draft. Bard’s attempt, on the other hand, got us excited about how the tool’s integration with Google capabilities we know and love.
Let’s try another one.
Bard, take it away!
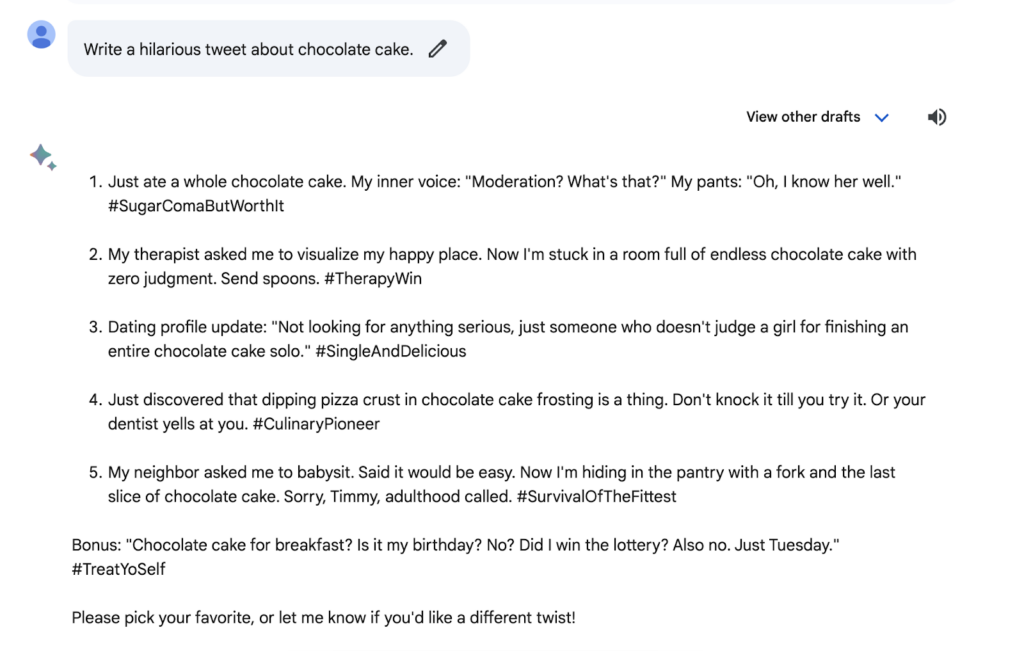
Your turn, ChatGPT.

You may want to collect yourself after laughing so hard.
In this experiment, we found it interesting that Bard went above and beyond by providing a number of options for tweets, while ChatGPT served up one.
Again, we stress that when it comes to comparing chatbots, your mileage may vary. If you were to conduct exactly the same tests, you will get an entirely different result. That’s the most salient point about generative AI–we’ve moved well past the era of predictable output. There is a tremendous degree of subjectivity when you’re deciding what tool is right for you. And remember–generative AI is always learning and growing the more that people use it. So results will be different not only from user to user, but for a single user over time.
Bard vs ChatGPT: how to decide between the two
Google Bard: pros and cons
Pros:
- Internet-powered responses: Bard offers built-in Internet access via Google Search, providing rapid responses to user queries.
- Effective information retrieval: Bard does a great job surfacing pertinent information, including images, from Google Search, enhancing the quality of responses.
- User-friendly interface: Bard’s user-friendly interface, featuring well-formatted, human-like responses, enhances the user experience.
Cons:
- Hallucination-prone: Bard is susceptible to generating inaccurate information, requiring users to exercise caution and cross-check responses.
- Reliability of sources: Bard’s sources can be questionable, necessitating the need to fact-check when using its information.
- Limited integrations: Bard provides a somewhat isolated experience, lacking support for plugins or integrations with other applications.
ChatGPT: pros and cons
Pros:
- Text generation expertise: ChatGPT is impressive at generating text, making it a valuable tool for creating long-form content and carrying out text-based tasks.
- Collaborative experience: ChatGPT allows users to share conversations with others, enhancing teamwork and communication.
- Plugin ecosystem: ChatGPT boasts a wide range of plugins and integration options, which expands its utility across different applications.
Cons:
- Web limitation: ChatGPT lacks access to a Web browser and relies on data sources with the cutoff year 2021, potentially limiting the freshness of its information.
- Lengthy responses: ChatGPT tends to generate lengthy and dense responses, making it challenging to quickly scan and extract information.
- Potential for inaccuracy: Like Bard, ChatGPT is not immune to generating inaccurate or hallucinatory content, putting the onus on human users for fact-checking and verification.
Considerations and caveats when using AI chatbots
AI chatbots can be incredibly helpful, but it’s essential to exercise caution and consider the following:
- Accuracy and reliability: AI chatbots might not always provide accurate or complete information. Double-check crucial details, and don’t solely rely on them for important decisions.
- Privacy concerns: Avoid sharing sensitive or personal information with chatbots unless you’re using a reputable and secure platform, especially when discussing financial or health matters.
- Contextual understanding: Chatbots can struggle with context, leading to misunderstandings or irrelevant responses. Make sure your questions are clear and concise.
- Bias and fairness: Chatbots can inherit biases from training data, potentially producing biased or discriminatory responses. Use them responsibly and be mindful of how groups and individuals are represented.
- Limited creativity: Chatbots operate based on patterns and data and may provide repetitive or formulaic responses, especially when it comes to creative tasks.
- Security risks: Maintain vigilance against malicious actors who might exploit chatbots for phishing or social engineering attacks. Avoid sharing personal or financial information without verification.
- Emotional support: While chatbots can offer some emotional support, they can’t replace human interaction, especially in situations requiring human-to-human empathy.
- Technical issues: Chatbots may experience technical glitches or downtime. Exercise patience and seek alternative ways to obtain information or assistance.
- Human touch: Overreliance on chatbots in customer service can lead to a lack of personalized human interaction. Consider the inherent value of human contact.
- Regular updates: AI chatbots require regular updates to stay relevant and effective. Keep an eye on developer updates and improvements.
- Legal compliance: Ensure your use of chatbots complies with applicable laws and regulations, especially in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
- Data privacy: Understand how the data you share with chatbots is stored and used. Check the platform’s privacy policy to know their data retention practices.
Should your organization use Google Bard or ChatGPT?
The decision between Google Bard and ChatGPT for your organization hinges on your specific needs and priorities. If your organization frequently requires access to real-time information and values seamless integration with Google services, Google Bard may be your preferred choice. Its multilingual support and current free access can also be advantageous. If your organization focuses on content generation or task completion, ChatGPT may be worth a look.
To make an informed decision, assess your use cases, language requirements, budget, integration needs, and customization requirements, all while considering data privacy and security concerns. Conducting pilot tests or trials may help determine which chatbot aligns best with your organization’s goals and operational requirements.
To learn the five key steps to pilot Duet AI, download the complimentary Gartner report today.
Google Bard and ChatGPT have different strengths, and both continue to grow and improve dramatically. Bard is great for research, real-time Web searches, and Google integration, while ChatGPT’scontent generation and task completion functions are impressive. The choice depends on your organization’s specific needs.
ChatGPT is a powerful AI chatbot, but its ”best” status depends on your specific criteria and use case. At this early stage, it’s worth trying out both chatbots to determine what works best for you.
Bard and ChatGPT are distinct AI chatbots with unique features and development origins.



