Cloud security solutions

In today's digital world, cloud security solutions are essential for safeguarding data in the cloud. Explore the vital technologies and practices that ensure secure and successful cloud computing.

What are cloud security solutions?
Cloud security solutions encompass a diverse array of tools and strategies crafted to safeguard data, applications, and the infrastructure housed within cloud computing environments. These solutions tackle the distinct security hurdles that arise in cloud computing, including issues like data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance obligations. Vital elements encompass identity and access management (IAM) for user oversight, encryption for shielding data, and threat detection systems for spotting and countering potential risks. Cloud security solutions are absolutely essential for upholding the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of digital assets in the ever-changing realm of cloud computing, fostering trust and assurance in cloud-based operations.
Cloud security solutions are designed to address various security issues presented by cloud environments, including:
Configuration risk: Configuration errors can be exploited by attackers. Cloud security solutions can help to identify and mitigate configuration risks.
Access: Cloud environments often have a large number of users and devices accessing them, making it more of a challenge to control access and prevent unauthorized access. Employing cloud security solutions can effectively manage access and mitigate unauthorized entry.
Compliance: Cloud security solutions can help organizations comply with regulations, such as data privacy laws.
Workload protection: Cloud security solutions help protect workloads from a variety of threats, such as malware and denial-of-service attacks.
Data protection: Cloud security solutions help protect data in cloud environments from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.

Why is cloud security important?
Cloud security is vital because it safeguards sensitive data and critical applications hosted in cloud environments. It prevents breaches, unauthorized access, and data theft, thereby protecting against financial losses and reputational damage. Strong cloud security measures are essential for maintaining trust, enabling digital innovation, and harnessing the benefits of cloud computing securely.

Common cloud security challenges
Common cloud security challenges include data breaches resulting from misconfigurations or cyberattacks, compliance complexities, difficulties in monitoring due to dynamic cloud environments, and the shared responsibility model's ambiguity. Addressing these challenges demands robust and adaptable cloud security solutions to protect data and maintain a secure cloud ecosystem. If you’re unsure of your cloud security posture, SADA’s security experts can help you discover your Cloud Security Score with a Cloud Security Confidence Assessment. We’ll evaluate your current controls and provide recommendations and best practices to help address security risks and prepare for today’s increasingly sophisticated threats.
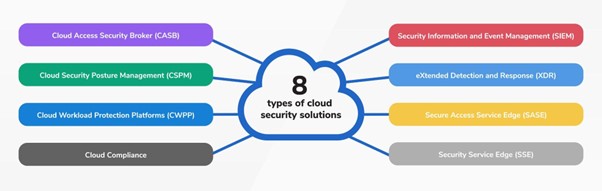
8 types of cloud security solutions
Cloud security is a multifaceted endeavor, and to effectively safeguard data and resources in the cloud, it's crucial to understand the eight key solution categories that play pivotal roles in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
1. Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
CASBs are tools that provide organizations with visibility and control over the use of cloud services and applications. They enable security policies, data protection, and threat detection for cloud environments, acting as intermediaries between users and cloud providers.
2. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM solutions help organizations assess and manage their cloud infrastructure's security posture. They identify misconfigurations, compliance violations, and vulnerabilities within cloud resources and offer remediation recommendations to maintain a secure environment. SADA offers a CSPM solution to assist you in setting up Google Cloud’s Security Command Center Premium (SCCP) and fine-tuning it in accordance with best practices while also integrating into your existing ecosystem.
3. Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP)
CWPP solutions focus on securing workloads and applications running in the cloud. They offer protection against malware, intrusion attempts, and data breaches by monitoring and safeguarding cloud-based applications and data.
4. Cloud Compliance
Cloud compliance solutions help organizations adhere to regulatory and industry-specific security requirements in the cloud. They automate compliance checks, report generation, and audit trails to ensure cloud operations meet necessary standards.
5. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) tools gather and scrutinize security data from a wide range of origins, encompassing cloud environments, with the aim of identifying and addressing security incidents. These tools offer capabilities for real-time monitoring of threats, issuing alerts, and conducting forensic analyses.
6. eXtended Detection and Response (XDR)
XDR solutions go beyond traditional threat detection by correlating data from multiple security sources, including cloud resources, to provide a more comprehensive view of security threats. They enhance threat detection and response capabilities across the entire organization.
7. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
SASE combines network security and wide-area networking (WAN) capabilities into a cloud-based service. It integrates security and networking functions, allowing secure access to cloud resources and applications from anywhere.
8. Security Service Edge (SSE)
SSE extends security protections to the edge of the network, offering security services close to users and devices. It provides consistent security for cloud and on-premises resources, enhancing protection for distributed environments.
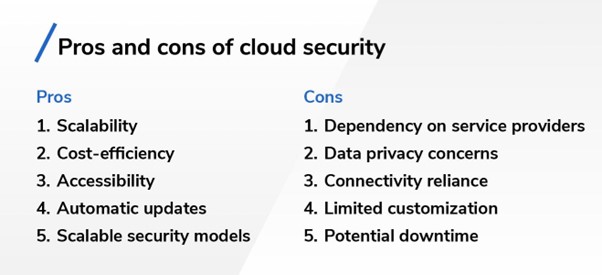
Pros and cons of cloud security
Cloud security, like any technological approach, is associated with a distinct set of pros and cons. Below are some of the primary advantages and disadvantages of implementing cloud security:
Pros
- Scalability: Cloud security solutions have the flexibility to effortlessly expand and adapt to the evolving requirements of organizations. As data and resource demands increase, cloud security can adapt accordingly, reducing the need for extensive hardware and software investments.
- Cost-efficiency: Cloud security often eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and maintain on-premises security infrastructure. This can lead to cost reductions in terms of hardware, software, and upkeep expenses.
- Accessibility: Cloud security solutions can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing for remote management and monitoring of security systems. This accessibility can enhance response times to security incidents.
- Automatic updates: Cloud security providers typically handle software updates and patch management, ensuring that security systems are up to date with the latest threat intelligence and vulnerability fixes.
- Scalable security models: Cloud providers offer a range of security services, allowing organizations to choose and customize the level of security that suits their needs, whether it's basic protection or advanced threat detection and response.
Cons
- Dependency on service providers: Organizations entrust their security to third-party cloud providers, which can create dependency and raise concerns about data control and privacy.
- Data privacy concerns: Storing sensitive data in the cloud can raise concerns about data privacy and compliance with regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA. Organizations must ensure cloud providers meet their specific data security requirements.
- Connectivity reliance: Cloud security relies on internet connectivity. In case of an internet connection disruption, it can briefly impact an organization's capacity to access and oversee security systems.
- Limited customization: While cloud security offers flexibility, it may not allow the same level of customization as on-premises solutions, which can be a drawback for organizations with highly specialized security needs.
- Potential downtime: Although cloud providers strive for high availability, outages can occur. Organizations should have contingency plans in place to address such situations.
While cloud providers invest heavily in security, breaches can still occur. Organizations must diligently monitor and manage their cloud security and not assume that the cloud is immune to threats.

SADA offers a comprehensive suite of cloud security solutions, including:
- Security Confidence Assessment: SADA's Cloud Security Confidence Assessment can help you strengthen your security posture and get the most out of Google Cloud's robust security features. The assessment evaluates your current controls and provides recommendations and best practices to help you reduce risks and prepare for threats.
- Security Enriched Foundation: SADA will help you design and deploy a hardened cloud configuration for a rock-solid security posture.
- Cloud Native Access Control: With SADA’s Cloud Native Access Control offering, you can rest assured that your security posture is aligned to the zero trust solution that’s right for your business. With expert implementation by a dedicated team from SADA, Cloud Native Access Control gives your teams secure access to critical apps and services, simplifies the experience for admins and users, and modernizes and improves your security posture.
- User & App Protection: SADA’s experts will conduct a walkthrough of reCAPTCHA Enterprise, evaluate your current infrastructure, and develop source code integrating reCAPTCHA into your web application to prevent and detect fraud.
- Cloud Security Posture Management: A dedicated SADA team, including a Cloud Security Engineer and Project Manager, will assist you in setting up and fine-tuning SCCP in accordance with best practices while also integrating into your existing ecosystem. A team of experts from SADA, including a Cloud Security Engineer and Project Manager, will help you set up and optimize SCCP according to best practices, as well as integrate it into your existing ecosystem.

Google Cloud tools/software
Google offers a number of cloud security tools and software, including:
- Security Command Center: Provides a centralized view of your security posture across Google Cloud Platform (GCP), helping you detect threats, assess and manage risks, and improve your security posture.
- Chronicle SIEM (Security information and event management) and SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation and Response): These tools help you collect, analyze, and respond to security threats. They do this by collecting data from a variety of sources, including logs, network traffic, and endpoint devices. They then analyze this data to identify potential threats. If a threat is identified, SIEM and SOAR can automatically take steps to mitigate the threat, such as blocking an attacker's IP address or quarantining an infected endpoint device.
- reCAPTCHA Enterprise: Helps you protect your website from spam, abuse, and fraudulent activity like scraping, credential stuffing, and automated account creation. It does this by verifying that users are human and not bots.
- Cloud Armor: A web application firewall (WAF) that helps protect your applications from distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. This is accomplished by filtering and blocking malicious traffic, and by rate-limiting legitimate traffic to prevent it from overwhelming your application.
- Cloud IDS (Cloud Intrusion Detection System): Helps you detect and block malicious traffic by monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, denial-of-service attacks, and malware infections.
- Cloud Firewall: Helps you control access to your cloud resources by allowing you to create and manage rules that specify which traffic is allowed to flow to and from your resources. This can help you protect your resources from unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
- Cloud DLP (Data Loss Prevention): Helps you protect your sensitive data by identifying and classifying it, and then monitoring and controlling how it is used and shared. It can help you prevent data breaches, comply with regulations, and protect your intellectual property.
- Secret Manager: A secure and easy-to-use system for storing API keys, passwords, certificates, and other sensitive data. It provides a single place to manage, access, and audit secrets across Google Cloud.
- Binary Authorization: Helps you ensure that only trusted code is deployed to your cloud environment. It does this by verifying the code's identity and source, and by checking that the code has not been modified.

Additional ISV tools/software
- Wiz: A cloud security posture management (CSPM) tool that helps you identify and remediate security risks in your cloud environment. It does this by scanning your cloud infrastructure for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and policy violations. It then provides you with a detailed report of the risks it finds, along with recommendations for how to fix them.
- Okta: A cloud-based identity and access management (IAM) platform that helps organizations manage and secure user access to applications and data. Okta provides a single platform for managing user identities, provisioning and deprovisioning users, and enforcing access policies. It also offers a variety of integrations with other cloud-based applications and services, making it easy to extend IAM capabilities across an organization's IT environment.
- Concourse Labs: This Security-as-Code platform helps to give organizations comprehensive visibility and control of cloud security and compliance risk.
- Palo Alto: Protects your networks from security threats using a variety of methods, including firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), antivirus software, vulnerability scanning, and user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA).
- Orca: Helps you automate your cloud security operations by providing a centralized view of your cloud security posture, and by automating the detection and remediation of security risks. It’s easy to use and can be integrated with a variety of cloud providers.
- Snyk: Helps you find and fix vulnerabilities in your open source dependencies by scanning your code for known vulnerabilities and then providing you with information on how to fix them. Snyk can be used for both static and dynamic analysis, and it supports a wide range of programming languages. It also offers a number of features that can help you manage your open source dependencies, such as dependency tracking and security alerts.
These are just a few of the many cloud security tools, solutions, and software available. The best solution for your organization will depend on your specific needs and requirements. Contact our team to learn how we can help you strengthen your organization to defend against all potential threats. Through our Security Confidence Program, you’ll identify emerging attack vectors, remain well-informed about changing regulatory environments and compliance requirements, and gain confidence that your cloud data, your customers, and your business are secure.
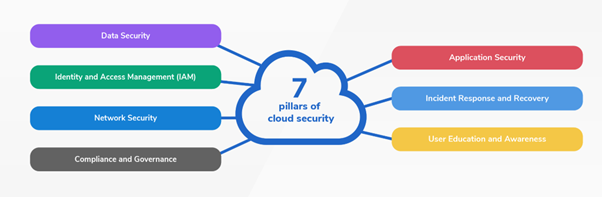
7 pillars of cloud security
There are several key pillars of cloud security that organizations should focus on to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and services. These key pillars include:
1. Data security
Data security solutions are designed to protect digital information from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. It involves implementing measures like encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention to safeguard sensitive and confidential data, ensuring its integrity and confidentiality in various computing environments. Data security is a fundamental aspect of cybersecurity, critical for both individual privacy and the protection of organizational assets.
- Data encryption: Data encryption constitutes a fundamental element of cloud data security. It encompasses the utilization of encryption algorithms to convert data into an indecipherable format, which can only be deciphered using the corresponding encryption key. This encryption is applied to data both during its transmission (in transit) and when it's archived (at rest). This dual-layered approach guarantees that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains safeguarded and incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): DLP technologies are designed to prevent the unauthorized sharing or leakage of sensitive data. They monitor data in transit, at rest, and in use, and enforce policies to block or quarantine data that violates security policies. DLP solutions are critical for protecting sensitive information from being inadvertently or maliciously exposed or shared outside the organization.
- Access control: Use robust access control mechanisms to restrict data access to authorized users and entities.
2. Identity and access management (IAM)
IAM is essential for controlling and managing user access to cloud resources. It involves defining and enforcing policies that determine who can access what, under what conditions, and from where. IAM solutions ensure that only authorized users and systems can access sensitive data and applications in the cloud, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. IAM includes:
- Strong authentication: Enforce strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identities of users and devices.
- Role-based access control (RBAC): Define and enforce roles and permissions for users, limiting access to necessary resources.
- Regular review: Continuously review and audit user access rights to ensure they align with the principle of least privilege.
3. Network security
Network security involves implementing measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, secure configurations, and encryption to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and resources within a network. Network security is essential for maintaining the reliability and security of communication and data transfer in both local and cloud-based networks, helping organizations protect their digital assets from various threats.
- Virtual private cloud (VPC): Implement network segmentation using VPCs or VNETs to isolate different parts of your cloud infrastructure.
- Security groups and network ACLs: Define and configure security groups and network access control lists to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) mitigation: Use DDoS protection services to safeguard against network attacks.
4. Compliance and governance
Compliance and governance refers to the enforcement of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure that an organization adheres to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and best practices.
- Compliance policies: Adhere to industry-specific compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and follow cloud provider-specific compliance frameworks.
- Audit trails and logging: Set up comprehensive logging and monitoring to detect and investigate security incidents.
- Risk assessment: Continuously assess security risks and vulnerabilities, and remediate any issues promptly.
5. Application security
Application security, often referred to as AppSec, is the practice of protecting software applications from security threats and vulnerabilities. It involves a set of measures, processes, and best practices aimed at ensuring that software is designed, developed, and deployed with security in mind.
- Secure development practices: Follow secure coding practices and conduct regular security code reviews.
- Web application firewalls (WAF): Use WAFs to protect web applications from common security threats.
- API security: Secure APIs and ensure proper authentication and authorization mechanisms.
6. Incident response and recovery
Incident response and recovery is a structured approach to addressing and managing cybersecurity incidents in a way that minimizes damage, reduces recovery time, and mitigates the impact of security breaches or incidents.
- Incident response plan: Develop a well-defined incident response plan outlining the steps to take when a security incident occurs.
- Backup and recovery: Regularly back up data and have a robust disaster recovery strategy in place.

7. User education and awareness
In the context of cybersecurity, the goal of user education and awareness training is to empower users to recognize potential security threats, make informed decisions, and take responsible actions to protect sensitive data and information.
- Security training: Educate your organization's users about security best practices and potential threats.
- Phishing awareness: Train users to recognize and avoid phishing and social engineering attacks.

How to choose cloud security software
Selecting the appropriate cloud security software is a pivotal choice for organizations seeking to safeguard their data and assets within cloud environments. Here are steps to lead you through the selection procedure:
- Assess your needs
Begin by understanding your organization's specific security requirements, including data sensitivity, regulatory compliance, and the cloud services you use.
- Identify security goals
Define your security goals and objectives, such as preventing data breaches, ensuring compliance, or protecting against specific threats like malware or insider threats.
- Consider deployment models
Decide whether your requirements align with on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid security solutions. The choice depends on your existing infrastructure and cloud strategy.
- Evaluate key features
Identify the essential features your cloud security software should have, such as identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, threat detection, and incident response capabilities.
- Vendor reputation
Research and assess the reputation and credibility of potential cloud security vendors. Look for well-established providers with a track record of delivering effective security solutions.
- Scalability
Ensure the software can scale to accommodate your organization's growth and changing needs. Scalability is vital for cloud environments where resources can quickly expand.
- Integration capabilities
Check whether the software can seamlessly integrate with your existing cloud infrastructure, applications, and other security tools. Integration simplifies management and enhances security.
- Compliance requirements
Verify that the software aligns with your regulatory compliance needs (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS) and provides features to help you meet those requirements.
- User-friendly interface
Take into account the software's user-friendliness. An intuitive interface streamlines configuration, monitoring, and management processes, decreasing the likelihood of human errors.
- Performance and resource impact
Evaluate the software's performance impact on your cloud resources. It should not significantly slow down or disrupt your cloud operations.
- Support and maintenance
Assess the level of customer support and maintenance provided by the vendor. Ensure they offer timely updates, patches, and responsive support for any issues.
- Cost considerations
Understand the pricing model, including upfront costs, subscription fees, and any additional charges. Consider the software's total cost of ownership (TCO) over time.
- Trial and testing
Whenever possible, take advantage of free trials or proofs of concept to test the software in your specific cloud environment. This hands-on experience helps you determine its effectiveness.
- Security community and resources
Check if the vendor has an active user community, resources like documentation and training, and a history of addressing security vulnerabilities promptly.
- References and reviews
Seek references from other organizations that have used the software and read reviews to gain insights into real-world experiences with the product.
- Scalability
Ensure that the software can scale to accommodate your organization's growth and changing needs. Scalability is vital for cloud environments where resources can quickly expand.
- Long-term viability
Consider the vendor's long-term viability and commitment to ongoing product development and support.
- Customization and flexibility
Assess whether the software allows for customization to meet your organization's unique security requirements.
FAQ
Cloud security solutions address security issues in cloud environments, such as configuration risk, access control, compliance, workload protection, and data protection. Cloud security solutions protect organizations from cyber threats and unauthorized access and are essential for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud-based resources.
LET'S TALK
Our expert teams of consultants, architects, and solutions engineers are ready to help with your bold ambitions, provide you with more information on our services, and answer your technical questions. Contact us today to get started.


